Elliptic Problems
 A
second order Ghost Fluid method is
proposed for the treatment of interface problems of elliptic equations with
discontinuous coefficients. By appropriate use of auxiliary virtual points,
physical jump conditions are enforced at the interface. The signed distance
function is used for the implicit description of irregular domain. With the
additional unknowns, high order approximation considering the discontinuity can
be built. To avoid the ill-conditioned matrix, the interpolation stencils are
selected adaptively to balance the accuracy and the numerical stability.
Additional equations containing the jump restrictions are assembled with the
original discretized algebraic equations to form a new sparse linear system.
Several Krylov iterative solvers are tested for the
newly derived linear system.
A
second order Ghost Fluid method is
proposed for the treatment of interface problems of elliptic equations with
discontinuous coefficients. By appropriate use of auxiliary virtual points,
physical jump conditions are enforced at the interface. The signed distance
function is used for the implicit description of irregular domain. With the
additional unknowns, high order approximation considering the discontinuity can
be built. To avoid the ill-conditioned matrix, the interpolation stencils are
selected adaptively to balance the accuracy and the numerical stability.
Additional equations containing the jump restrictions are assembled with the
original discretized algebraic equations to form a new sparse linear system.
Several Krylov iterative solvers are tested for the
newly derived linear system.
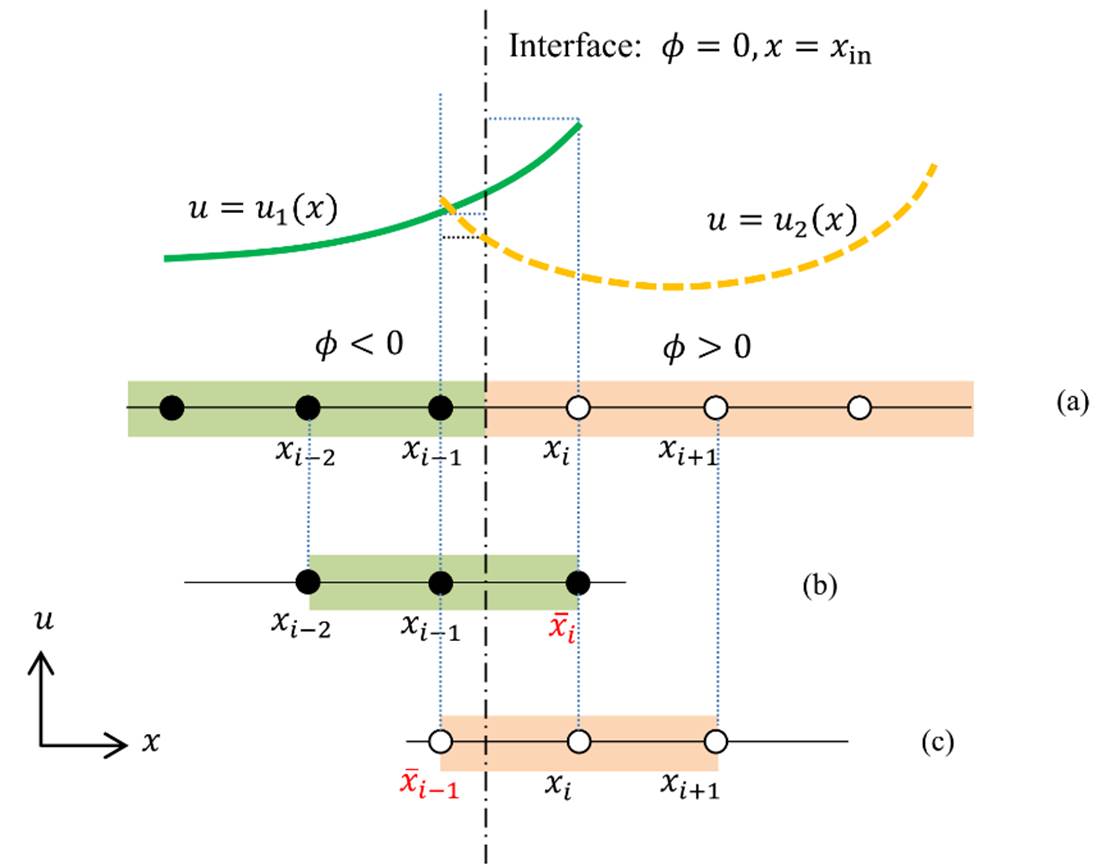
Fig. 1
One dimensional interpolation scheme for jump conditions.
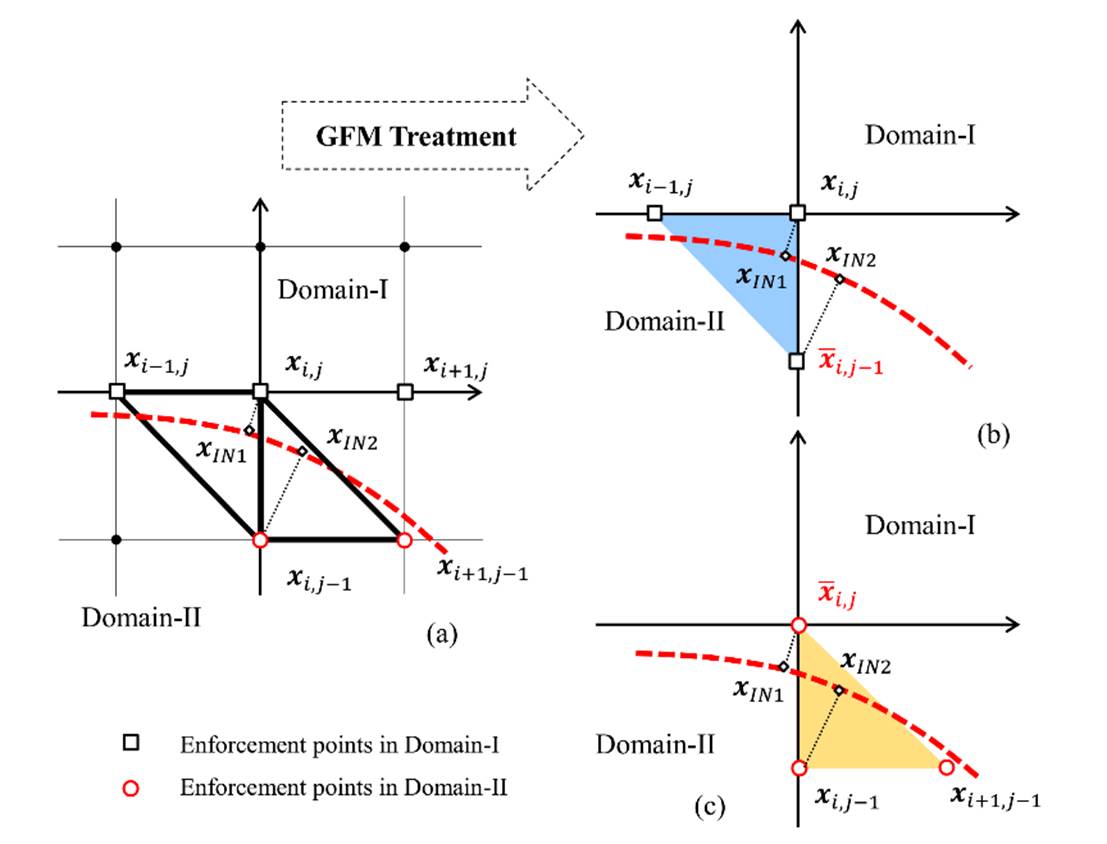
Fig.
2 Classification of the points for
construction of jump conditions. (a) Original enforcing points of the two
domains, (b) Interpolation stencils for domain-I, (c) interpolation stencils
for domain-II.
Table. 1 Average
error![]() and
maximum error
and
maximum error![]() .
.
|
|
Present
GFM method |
Previous
GFM method (Liu and Fedkiw, 2000) |
||||||
|
|
order |
|
order |
|
order |
|
order |
|
|
|
2.8790E-3 |
- |
5.8066E-4 |
- |
1.5300E-2 |
- |
5.4000E-3 |
- |
|
|
5.5882E-4 |
1.932 |
1.4639E-4 |
1.992 |
8.1000E-3 |
0.920 |
2.2000E-3 |
1.300 |
|
|
1.3707E-4 |
2.019 |
4.0393E-5 |
1.904 |
4.4000E-3 |
0.880 |
9.0000E-4 |
1.290 |
|
|
4.0929E-5 |
1.830 |
1.0532E-5 |
1.958 |
2.3000E-3 |
0.940 |
3.0000E-4 |
1.590 |
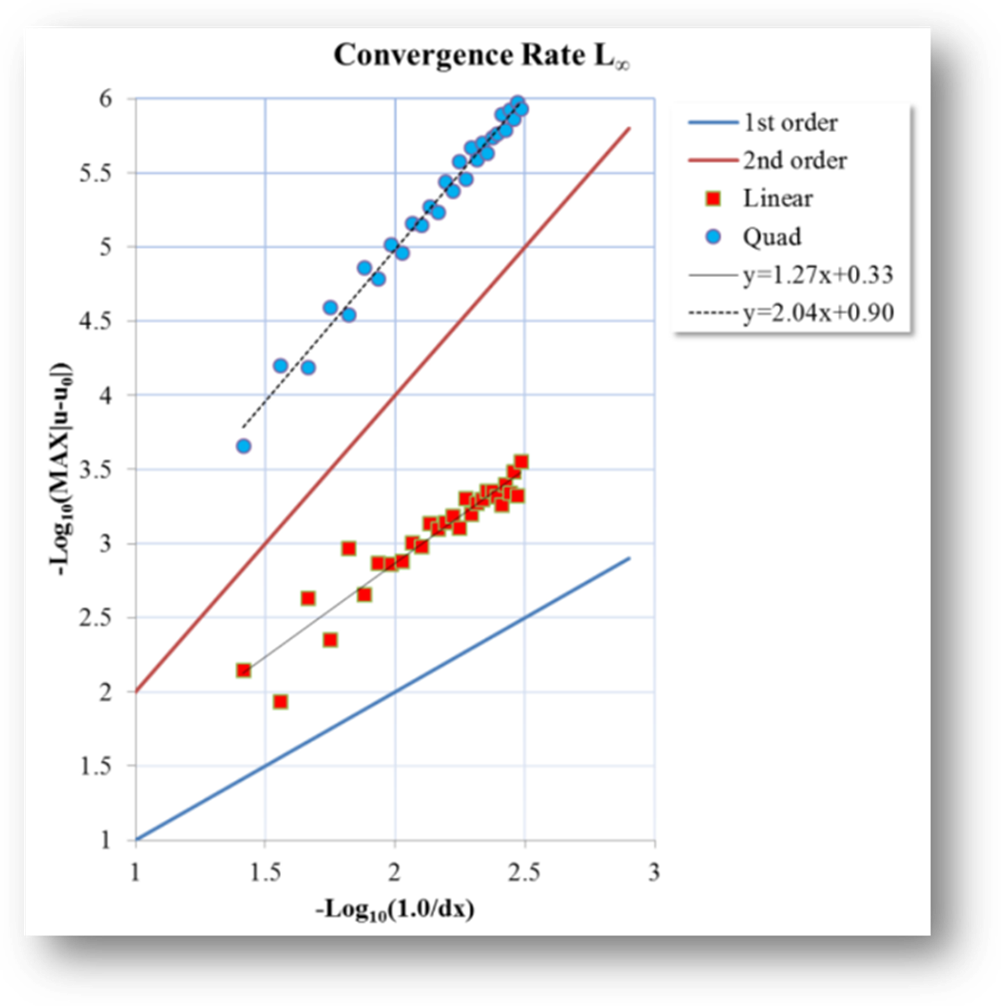
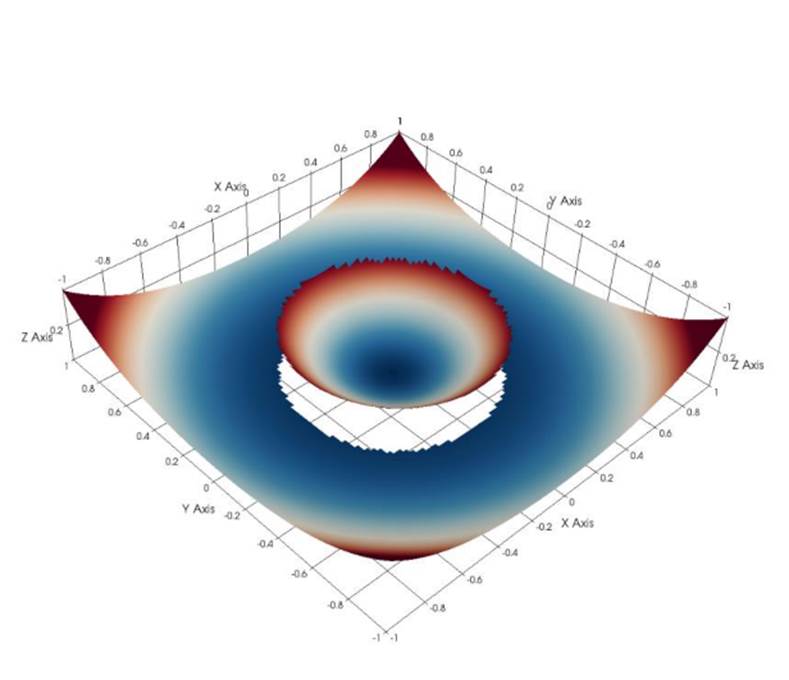
Fig. 3 Numerical
accuracy tests for an elliptic problem.
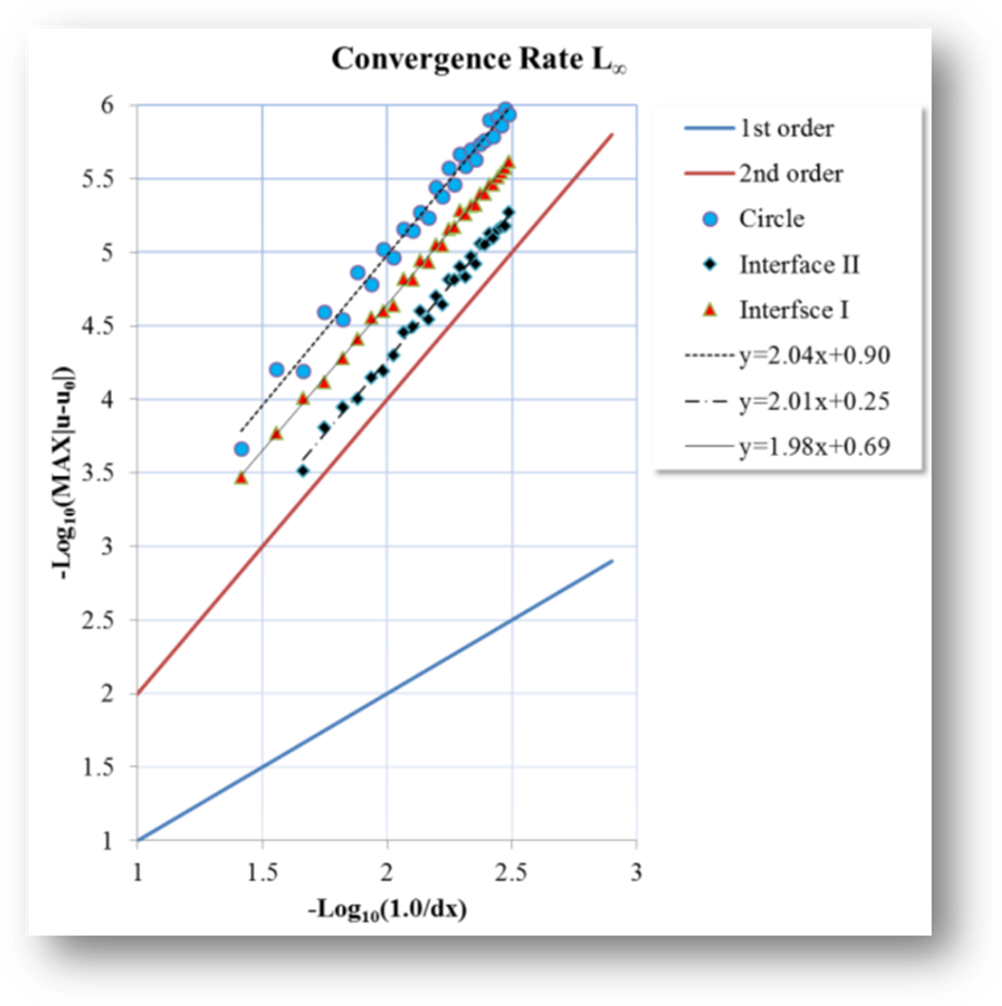
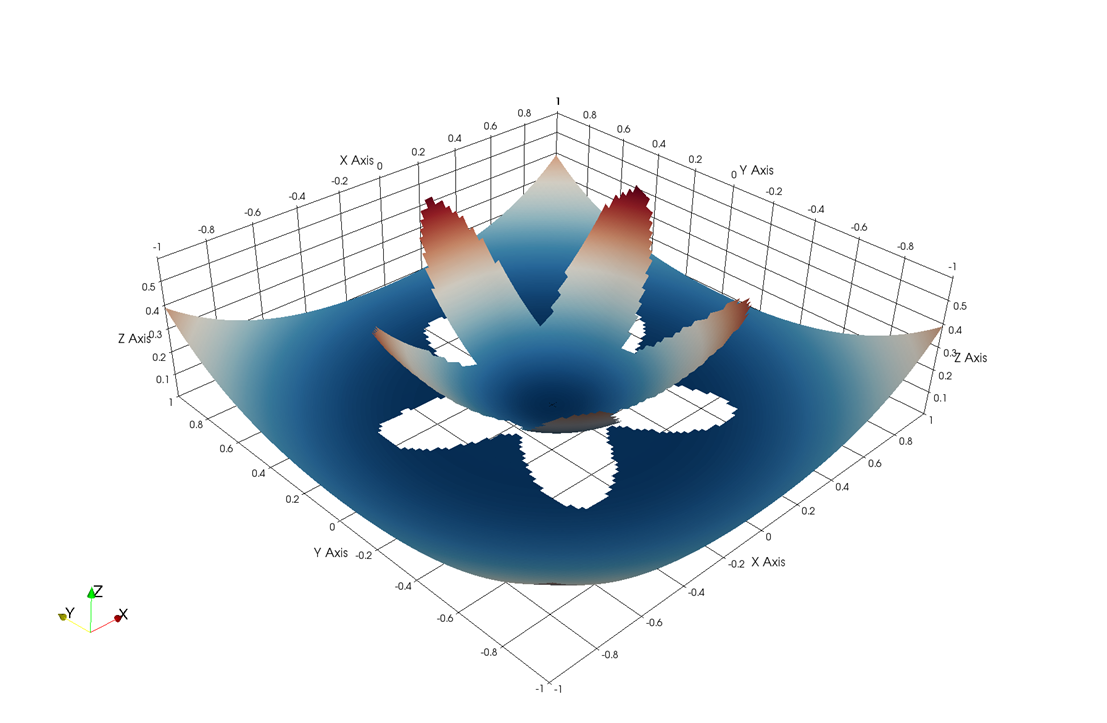
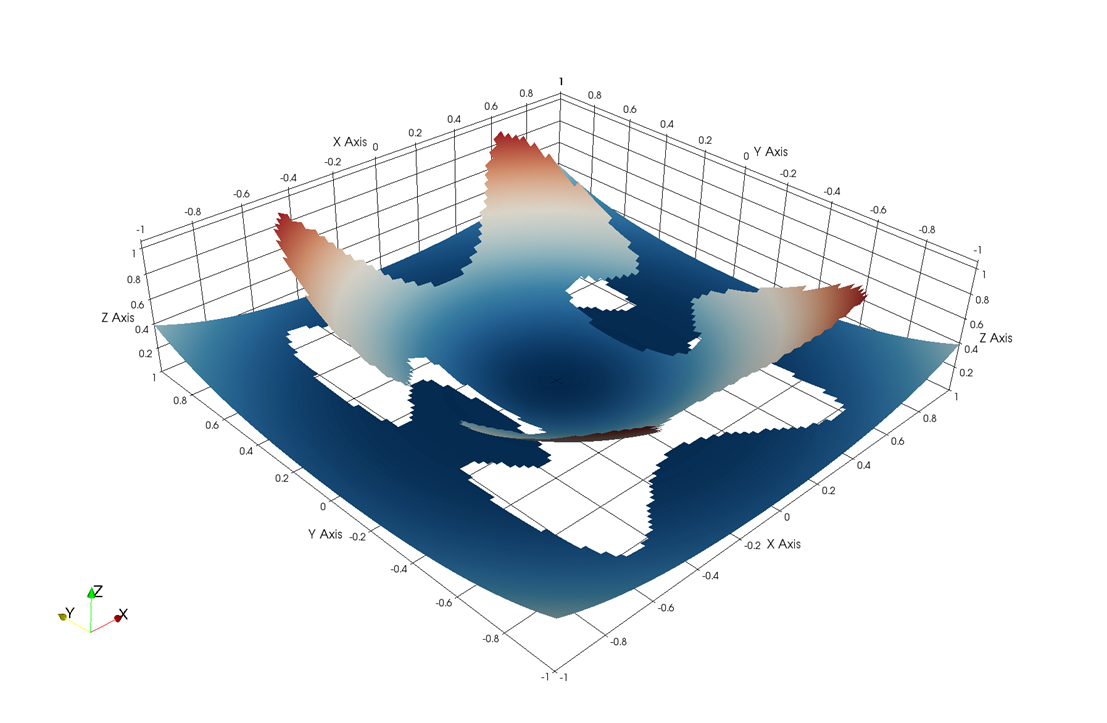
Fig. 4 Numerical
accuracy tests for two elliptic problem with irregular interface shape.
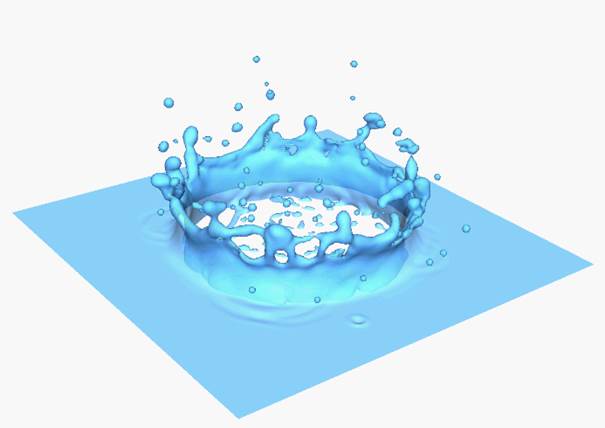
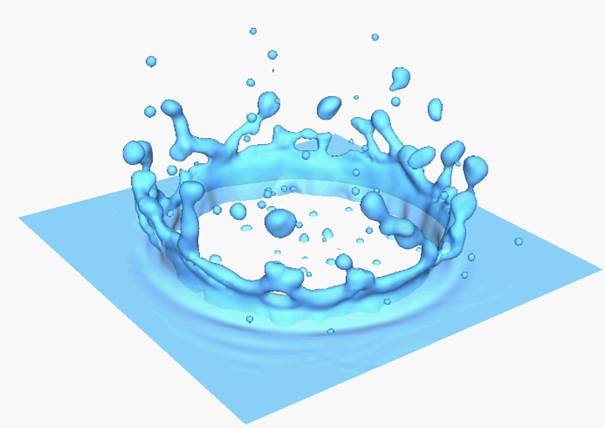
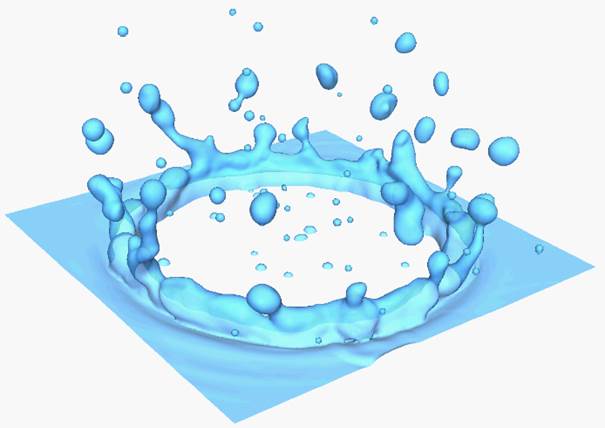
GFM for Two Phase Flows (Sharp Interface Method)
Droplet
Impaction



Reference
C. Liu*, C.
Hu, A Second Order Ghost Fluid Method for an Interface
Problem of the Poisson Equation, Communications in Computational Physics,
(2017), 22(4):
965-996.